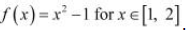By Rolle’* Theorem, for a function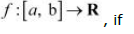
(a) f is continuous on [a, b]
(b) f is differentiable on (a, b)
f (a) = f (b)
then, there exists some c ∈ (a, b) such that f'(c) =0
Therefore, Rolle’* Theorem is not applicable to those functions that do not satisfy any of the three conditions of the hypothesis.
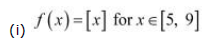
It is evident that the given function f (x) is not continuous at every integral point. In particular, f(x) is not continuous at x = 5 and x = 9 ⇒ f (x) is not continuous in [5, 9].
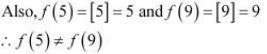
The differentiability of f in (5, 9) is checked as follows. Let n be an integer such that n ∈ (5, 9).
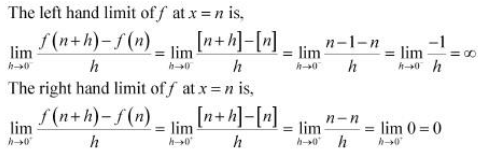
Since the left and right hand limits of f at x = n are not equal, f is not differentiable at x = n
∴f is not differentiable in (5, 9).
It is observed that f does not satisfy all the conditions of the hypothesis of Rolle’* Theorem.

It is evident that the given function f (x) is not continuous at every integral point. In particular, f(x) is not continuous at x = −2 and x = 2 ⇒ f (x) is not continuous in [−2, 2].
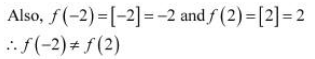
The differentiability of f in (−2, 2) is checked as follows. Let n be an integer such that n ∈ (−2, 2).
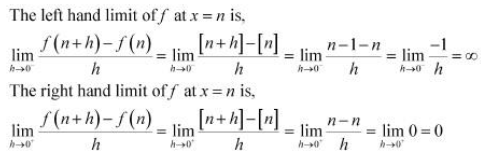
Since the left and right hand limits of f at x = n are not equal, f is not differentiable at x = n
∴f is not differentiable in (−2, 2).
It is observed that f does not satisfy all the conditions of the hypothesis of Rolle’*
Theorem.
Since the left and right hand limits of f at x = n are not equal, f is not differentiable at x = n
∴f is not differentiable in (−2, 2).
It is observed that f does not satisfy all the conditions of the hypothesis of Rolle’*
Theorem.
Hence, Rolle’* Theorem is not applicable for 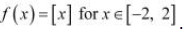
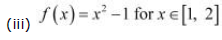
It is evident that f, being a polynomial function, is continuous in [1, 2] and is differentiable in (1, 2).
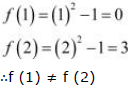
It is observed that f does not satisfy a condition of the hypothesis of Rolle’ Theorem.
Hence, Rolle’ Theorem is not applicable for