Introduction : Law of demand is one of the important basic laws of consumption. Prof. Alfred Marshall, in his book “Principles of Economics”, has explained the law of demand as follows :
Statement of Law : “Other things being constant the higher the price of the commodity, smaller is the quantity demanded and lower the price of the commodity larger is the quantity demanded.”
The law of demand explains change in the behaviour of consumer demand due to various changes in price.
Marshall’* Law of demand describes functional relation between demand and price. It can be expressed as D = f (P), that is demand is function of price. The relation between price and demand is inverse, because larger quantity is demanded when price falls and smaller quantity is demanded when price rises. The law of demand is explained with the help of the following schedule and diagram :
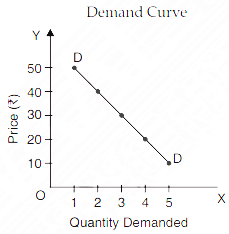
Table No. - Demand Schedule
| Price of Mangoes Per Kg. (Rs.) | Demand for Mangoes(Kg.) |
| 50 | 1 |
| 40 | 2 |
| 30 | 3 |
| 20 | 4 |
| 10 | 5 |
As shown in the schedule when price of mangoes is Rs. 50/- per kg., their demand is 1 kg. When price falls to the level of Rs. 40/- per kg. and demand rises to 2 kg. Similarly, at the price Rs. 10/- per kg., demand of mangoes is 5 kg., whereas 4 kg. of mangoes are demanded at price Rs. 20/- per kg. This shows inverse relation between price and demand.
In this diagram, X-axis represents demand for mangoes, whereas Y-axis represents price of mangoes. DD is demand curve which slopes downwards from left to right. In other words, its slope is negative because of inverse relationship between price and demand.
The law of demand is based on the following assumptions :
(i) Size and composition of population **** constant : There should not be any change in the size and composition of population. Because a change in population will bring about a change in demand even if price **** the same.
(ii) Income of the consumer : The income of the consumer is assumed to be constant.
(iii)Taste and preferences : These should not be any change in the tastes, preferences and habits of the consumers.
(iv) Future price expectations : In future, price are expected to be constant. No change in future prices are expected.
(v) Price of the related goods : The prices of substitute and complementary goods are taken to be constant.
(vi) Govt. Policy : No change in govt. policy of taxation should be there.