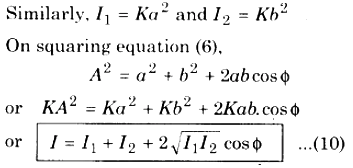Interference of Two Waves:
“When the two waves of same frequency coming from coherent sources and travelling in same direction, superimpose each other, the resultant intensity, in general, is different from the sum of individual intensities of the waves. At some places, the resultant intensity is greater then the sum of individual intensities and at some other places, resultant intensity is less than the sum of individual intensities. The event of this rise and fall in resultant intensity, in the region of superimposition, is known as ‘Interference’.
Where the resultant intensity is greater than the sum of individual intensities, the interference taking place there is called “Constructive interference’. On the other hand, where the resultant intensity is less than the sum of individual intensities, the interference taking place there is called “Destructive interference”.
Mathematical Analysis : Suppose the equations of two waves of same frequency (ω = 2πn) are as under :
y1 = a sinωt ………… (1)
and y2 = b sin(ωt + ϕ) ……………. (2)
Where a and b are the amplitudes of the waves and (ϕ) is the phase difference between them. If these waves superimpose each other,then from the principle of superimposition,
y = y1 + y1
or y = a sin ωt + b sin(ωt + ϕ)
= a sinωt + b sinωt cosϕ + bcosωt sinϕ
= (a + b cosϕ) sin ωt + b sin ϕ. cos ωt
or y = A cosθ.sinωt + A sinθ.cosωt
Where A cosθ = a + b cosϕ ……….. (3)
and A sinθ = b sin ϕ) ……….. (4)
∴ y = A [sinωt cosθ + cosωt sinθ]
or y = A sin [ωt + θ] ……….. (5)
This is the equation of resultant wave where A is its amplitude.
Resultant Amplitude : To get the resultant amplitude, on adding the squares of equation (3) and (4),
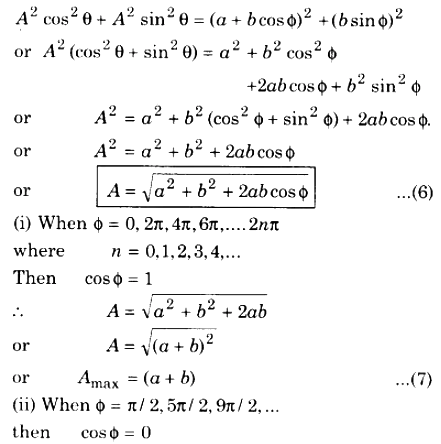
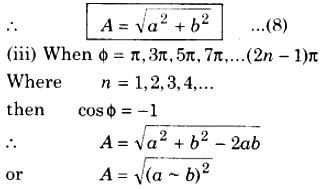
or, A = (a ~ b) ………….. (9)
or, Amin = (a ~ b)
Similarly other values of A can be calculated.
Resultant Intensity :
∵ Intensity ∝ (Amplitude)2
∴ I ∝ A2 or I = KA2